Curing Salt Substitutes: 4 Alternatives
2021-03-15(133377)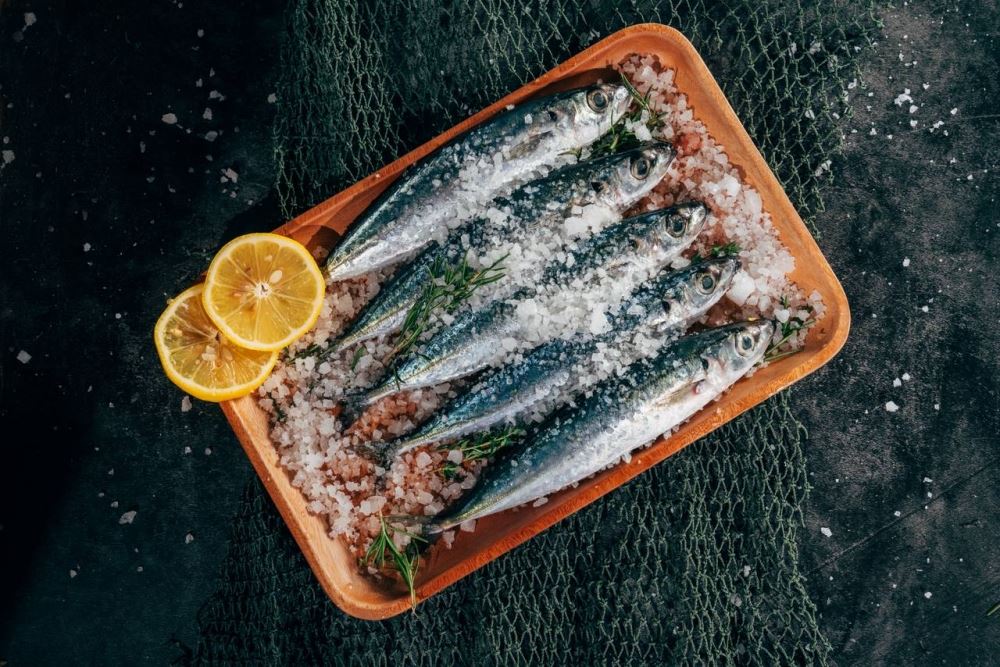
Curing salt’s purpose is preventing food related sicknesses and preserving by killing microbes in the food. It contains sodium nitrate breaking down into sodium nitrite, which dries out the moisture that the bacteria need. There are different types of curing salt which are very effective for preservation, but sometimes you may need a curing salt substitute.

Curing salt was formulated as a preservative primarily for meat and its side products. Its main ingredients may vary from product to product but it typically contains a mixture of high grade salt, sugar, curing agents like sodium nitrate and sodium nitrite and propylene glycol to keep the mixture intact. Curing salt is generally dyed a pink color so that it can be easily separated from regular salt.
History of Curing
Curing is an ancient technique as meat was originally preserved by covering the meat with salt. The method can be traced as early as to the Sumerian culture, 4,000 BC.
Researches suggest that the salt used meat curing in ancient times was contaminated with salt peter/potassium nitrate. It created a desirable red color after mixed with meat. It was also discovered that curing salt could also provide a longer storage life. After many developments, the additional multifunctional benefits of curing ingredients to meat were well-recognized.
The term "cure" can be used as a noun or a verb. “To cure" means adding nitrite and/or nitrate with salt to a meat product to provide preservation, meaning the terms "curing" or "cure" are used typically when nitrite and/or nitrate are added to a meat product.

Meat curing is associated with processed meats for the purpose of altering color and flavor as well as food safety and preservation. Curing process changes the meat, resulting in unique products which are different from fresh meat products.
There are many health safety concerns about curing salt. As it is some kind of an altering process, it is commonly believed that curing salt creates chemicals that are harmful to health. Even though many regulations has been implemented on curing products and their ingredients, many people still look for curing salt substitutes. Koyuncu Salt is among world’s biggest salt providers, and now it is time to discover alternatives to curing salt.
Saltpeter

Saltpeter is also known as potassium nitrate. It has been used as preservative since the Middle Ages. Nowadays, saltpeter’s use as a preservative is largely avoided due to inconsistent results; however, it is a good agent to use for homemade meat preservation.
Similar to curing salt, saltpeter draws moisture out of meat. It applies both to the cells of the meat and the cells of any bacteria in the meat, killing the bacteria. In other words, it provides the same preservative benefits as curing salt. You can use it to cure meats that you cook later on.
Non-iodized Sea Salt

Nitrates are not the only substances to cure your meat. It can be done with simple sea salt, which also draws water out of the cells. The curing could be done with any kind of salt, but experts recommend avoiding iodized salt. While iodized salt would still have the preservation properties, the iodine it contains can give the cured meat an unpleasant taste. In addition to this, table salt may slow down cooking and that may affect the taste or leave a sediment in the brining liquid.
Keep in mind that if you decide to use a nitrate-free cure, you should know that there is an increased risk of bacteria pathogens left. For this reason you should cure meat for a shorter time to limit bacterial growth.
Celery Juice or Powder

Celery juice or powdered celery juice are both used in commercially made nitrate-free cured meats. This is done in order for producers to mark their goods as nitrate-free. Celery juice is used because it naturally contains high amounts of nitrates, which is why it is possible to make a nitrate-free label for the products because it is an organic element. But the FDA accepted celery juice or powder as a flavoring agent, not as a preservative.
You can use celery juice or powder as a substitute for curing salt. However, remember that this curing method is imprecise because without checking the meat in which the celery juice is used, it is difficult to know how high the nitrate content is.
Raw Sugar

Raw sugar/turbinado sugar is another common ingredient used in naturally-cured products. Turbinado sugar is extracted from sugar cane juice evaporation, accompanied by centrifugation to eliminate molasses. However, there is no clear evidence on substantial amounts of nitrate or nitrite are found in raw sugar.