Kosher Salt: What’s special about kosher salt? Why It’s Called Kosher?
2020-08-17(40842)
You might have realized that edible salt is sold in different forms in the market. So, when shopping for salt, you might even have said “Why are there too many types? Salt is salt anyway.” If you are not used to trying different edible salt types, you might be wondering. Well, being an essential nutrient and a basic taste for food, edible salt is available in different forms such as sea salt, iodized salt, table salt, rock salt, and kosher salt.
The difference between salt types is their texture, flavor, source, degree of processing, and the method used in that process. Some salt types get their name from the place they originate such as Celtic salt. Celtic salt earns its name from Celtic Sea marshes in Brittany, France where it is produced through a solar evaporation method.
Now, if you reread these different edible salt types, almost all of them hint at their difference and meaning, but almost. There is one salt type in this list that needs clarification: kosher salt.
What is Kosher Salt?

Time to answer your questions about kosher salt; What does kosher salt mean? Kosher salt has a larger grain size compared to table salt which consists of small and easily dissolvable grains. It is easy to observe the size difference between table salt and kosher salt. Kosher salt has free of additives but may include anti-caking agents.. Kosher Salt is used in the Jewish religious practise of dry brining meats, known as kashering and some brands has kosher-certified salt as being approved by a religious body.
How Kosher Salt Is Made
Salt is a naturally occurring mineral primarily composed of sodium chloride (NaCI). It can be harvested from salt rocks or salt mines or produced through evaporation of salt lakes and seawater or brine. Once the water is evaporated, only salt crystals remain which can be processed differently for each various usage areas.
Did you know that salt has a lot of usage areas besides for food such as industrial salt, pool salt, road salt, water treatment salt and animal salt? Now you do. Additionally, kosher salt can be produced by salt companies which have Kosher certification like Turkey’s reliable salt manufacturer Koyuncu Salt which produces different edible salt types such as salt for the food industry, kosher salt, and halal salt naturally from the Salt Lake.
Why Is It Called Kosher Salt?
It is the name of this salt type making us ask the questions. I mean “why is it called kosher salt?” and how kosher salt got its name. Your guess is probably that this type of salt is called kosher salt because of the Jewish dietary guidelines. However, the case is not so. In fact, although some salt that is sold in the market with the label of “kosher salt” can be not kosher at all!
Kosher salt gets its name from the purpose of koshering the meat. Koshering the meat means removing the blood from the meat. As I mentioned earlier, kosher salt has large grains or flakes. Its large grains make it easier to stick to meat chunks and therefore draw out the liquid and blood from it. Yet, because some salt companies labeled the coarse koshering salt packages as “kosher salt”, the name stuck. So, any salt can be kosher, but not all salt is “kosher.”
Kosher Salt vs. Regular Salt
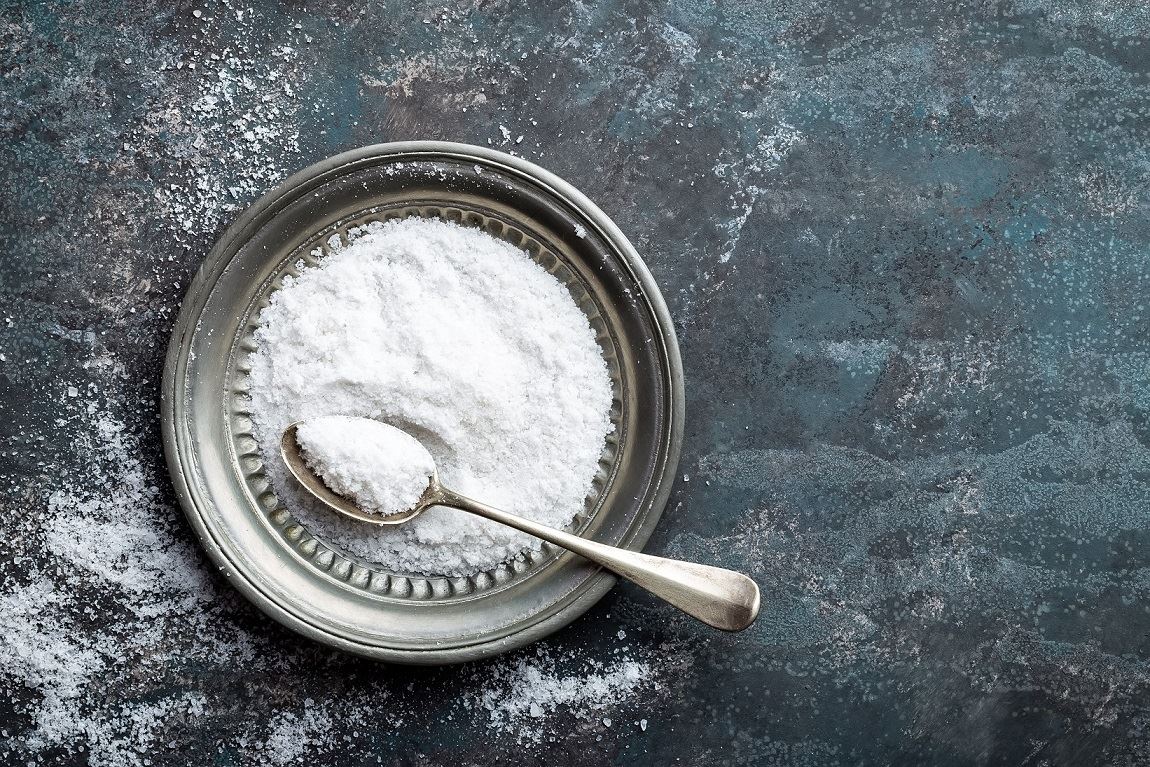

Imagine you are trying out a new recipe that you are really excited about. But you see there is kosher salt in the recipe. Then, it makes you think “What is the difference anyway?” and add regular salt instead. However, when you compare kosher salt vs salt, the two are very different, and you might end up with food that is too salty or bland. The difference between kosher salt and table salt is texture, grain size, production process, additives used, and thus the taste.
Kosher salt has larger flaky crystals with large surfaces, and it is easy to pinch with fingers. Due to its large grain size, it takes longer to dissolve in food and water compared to free-flowing table salt. Because of this, kosher salt is not commonly preferred in baking. Some kosher salts may consist of additives like anti-caking agents, but most are said to be free of additives.
In contrast, table salt consists of many additives to enhance the flavor. The most common salt additive is iodine. Moreover, since table salt has smaller grains, in their natural form they may easily stick together. Salt companies use anti-caking agents to prevent the grains from sticking together.
What are common additives to salt?
- Calcium aluminosilicate
- Calcium carbonate
- Calcium silicate
- Fatty acid salts (acid salts)
- Magnesium carbonate
The list can get even longer, however, in short, kosher salt does not contain these additives. Also, Kosher salt is free of iodine. Kosher salt vs regular salt is quite different considering these, aren’t they? Then there comes the question: what is a good substitute for kosher salt?
What Is A Good Kosher Salt Substitute?
Back to that new recipe you want to try out or your favorite recipe which requires kosher salt in its ingredients. You may have run out of kosher salt or have no time to go to the store to buy some. In this case, don’t worry there are alternatives to kosher salt. Let’s see your options for kosher salt substitute.
Coarse Sea Salt
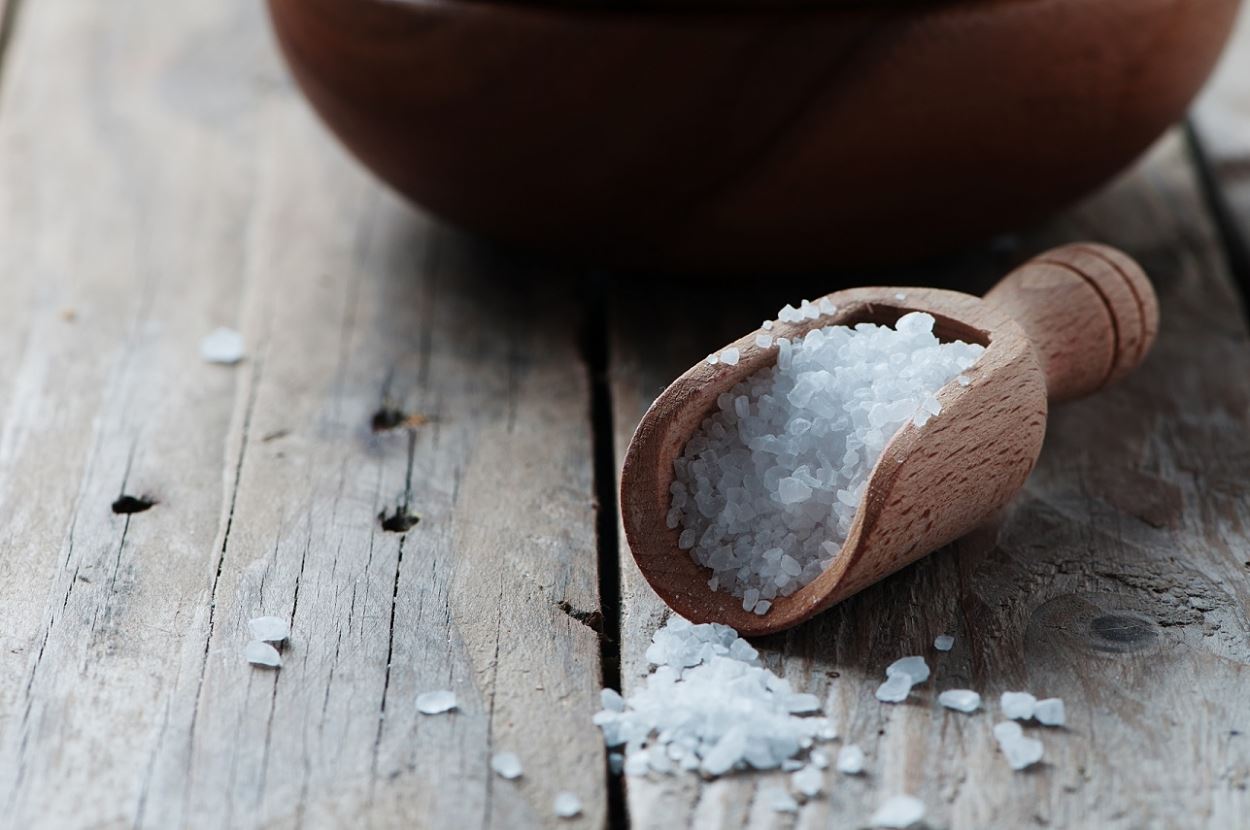

Some dishes may require kosher salt for its flaky texture and flavor. Sea salt resembles kosher salt in terms of coarse and large crystals. This makes coarse sea salt a perfect substitute for kosher salt. You can get the same texture and crunch. Besides, the flavor of sea salt is almost identical to kosher salt which makes it your best bet at kosher salt substitute. Sea salt is produced through salt lakes or seawater.
The size of crystals of kosher salt and coarse sea salt differs although slightly. This is why the amount of sea salt you use as a kosher salt substitute is quite important.
- You may add a single teaspoon of coarse sea salt for every 1 1/4 teaspoon of kosher salt according to your recipe’s requirements.
Pickling Salt
Pickling salt differs in texture from kosher salt. However, if flavor resemblance is what you are looking for rather than the coarse texture, then pickling salt is a good kosher salt substitute for you. Moreover, since pickling salt has finer grains, it quickly dissolves in pickling brine. And so will it in food. Considering these, pickling salt is a good kosher salt replacement. Yet, as with the sea salt, you need to adjust the amount you use.
- You may add a teaspoon of pickling salt for every 1 1/14 teaspoon of kosher salt according to your recipe.
Himalayan Pink Salt
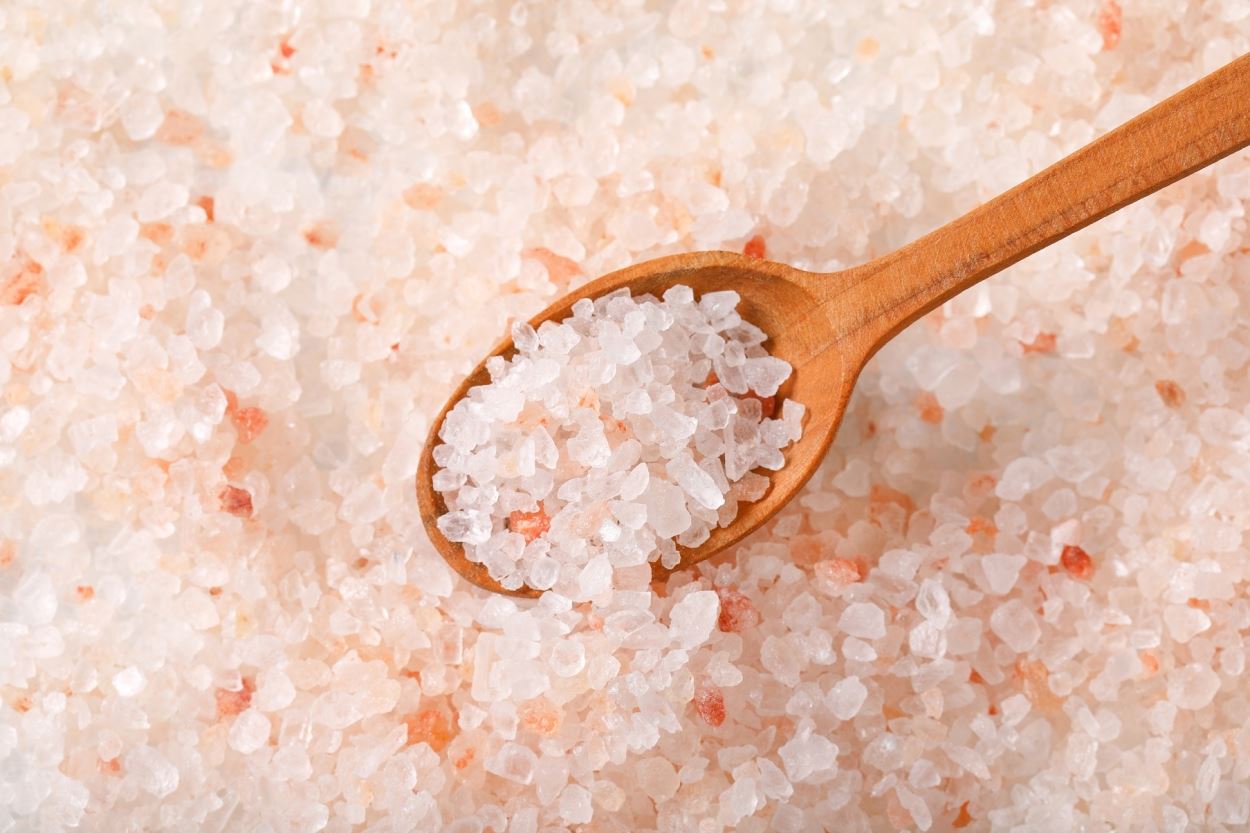

Some may prefer kosher salt because of its finishing touch on food which has a visually pleasing effect with its large flaky grains. But if you run out of kosher salt, you may use Himalayan pink salt as a substitute for kosher salt just as well. Himalayan pink salt will give your recipe the aesthetic finishing you need.
Moreover, Himalayan salt adds crunchiness just like kosher salt with its large grains. The obvious difference between the two is the pink color of the Himalayan salt. Why is Himalayan salt pink? It is because this type of salt contains trace amounts of rust in it which gives the pink color. Plus, it has iron oxide and trace amounts of other salt minerals.
The Bottom Line
Now that we have covered what is kosher salt, how kosher salt is made, why is it called kosher salt, kosher salt vs salt, and finally what is a good substitute for kosher salt, you can try out the substitutes we mentioned in your recipes and enjoy it!